Cluster Management
Create and manage multiple clusters in your Prediction Guard platform to organize your infrastructure based on teams, environments, or use cases.
Creating a New Cluster
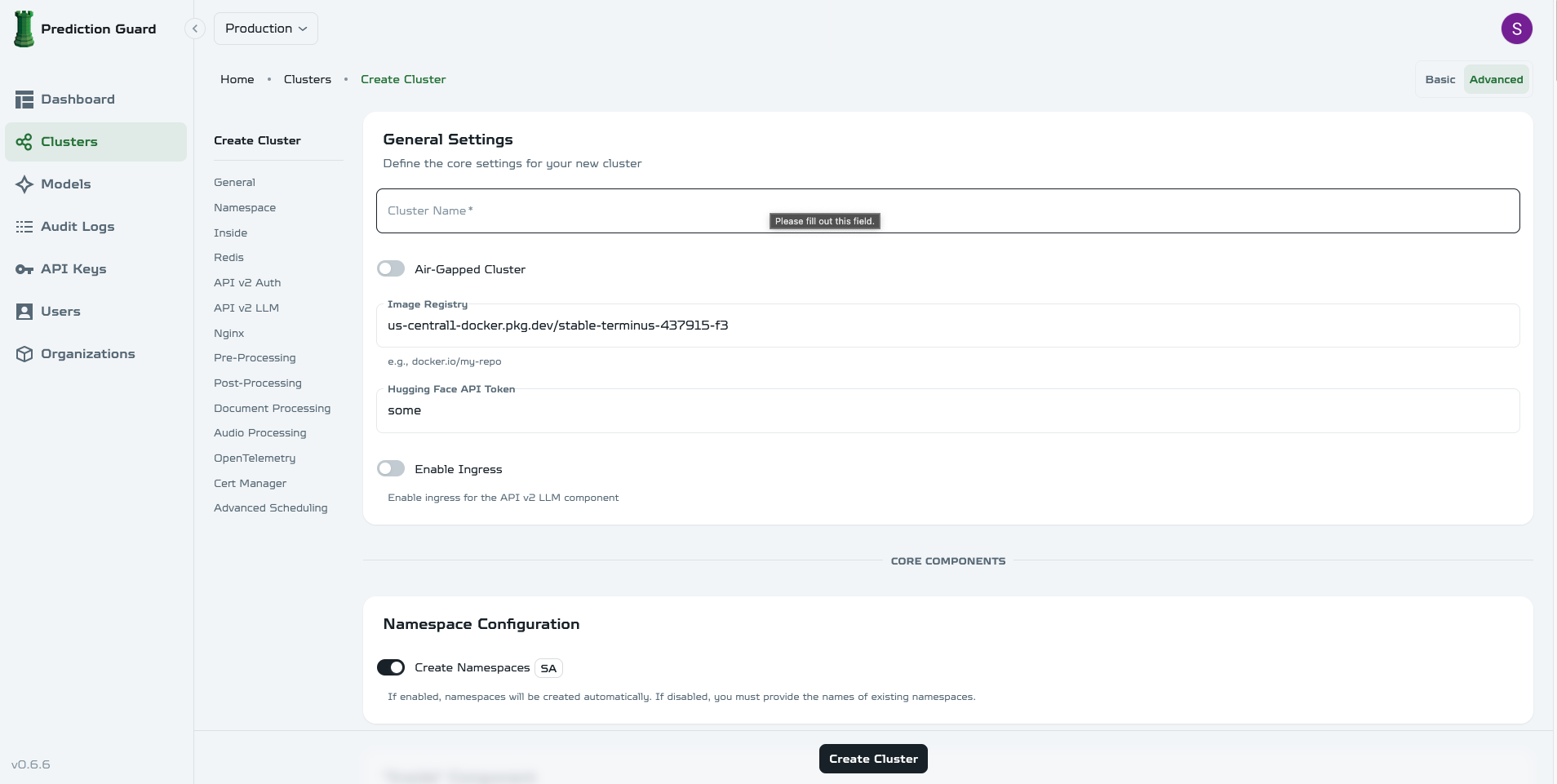
General Settings
When creating a new cluster, configure these basic settings:
- Cluster Name: A descriptive name for your cluster (required)
- Air-Gapped Cluster: Enable for offline deployments
- Image Registry: Docker registry for container images
- Hugging Face API Token: Token for accessing Hugging Face models
- Enable Ingress: Enable external API access
Core Components
Namespace Configuration
- Create Namespaces: Automatically create required namespaces
- Custom Namespaces: Use existing namespaces if disabled
Inside Component
- Use Default Inside Image: Use standard Prediction Guard image
- Custom Image: Configure custom container image
- Service Account: Enable automatic service account creation
- Service Account Name: Name for the service account
Advanced Configuration
The cluster creation interface includes additional configuration sections:
- Redis: Cache and session storage configuration
- API v2 Auth: Authentication service settings
- API v2 LLM: Language model API configuration
- Nginx: Web server and load balancer settings
- Pre-Processing: Input processing pipeline
- Post-Processing: Output processing pipeline
- Document Processing: Document handling capabilities
- Audio Processing: Audio model support
- OpenTelemetry: Monitoring and observability
- Cert Manager: SSL certificate management
- Advanced Scheduling: Kubernetes scheduling options
Managing Existing Clusters
Cluster Overview
- Health Status: Monitor cluster health and performance
- Resource Usage: Track CPU, memory, and GPU utilization
- Model Status: View deployed models and their status
- Activity Logs: Review recent cluster activity
Basic Operations
- View Clusters: See all your clusters and their status
- Edit Configuration: Modify cluster settings
- Scale Resources: Adjust resource allocation
- Deploy Models: Add models to the cluster
- Monitor Usage: Track performance and costs
Best Practices
Cluster Organization
- Naming Convention: Use descriptive names for easy identification
- Environment Separation: Keep development and production separate
- Resource Planning: Plan resources based on expected workloads
- Documentation: Document cluster purposes and configurations
Security
- Access Control: Implement proper access controls
- Network Security: Use secure network configurations
- Regular Updates: Keep clusters updated with latest versions
- Monitoring: Set up comprehensive monitoring and alerting

